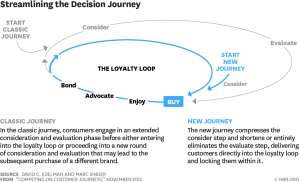
Reading a recent article in the Harvard Business Review on the topic of “customer journeys” got me thinking about their role in the association space.
What is a “customer journey”?
The example HBR used was of a solar company. Their initial outreach to one of the authors was a custom mail piece with a personalized URL that led him to a Google Earth image of his own house with solar panels mocked up on the roof. Clicking on that led to a webpage with estimates of potential energy savings, which then led to a one-on-one interaction with a sales rep to answer questions about leasing versus buying and installation. The company then sent references who were neighbors of the author, and a single-click lease tailored to his needs. The author was able to track progress of permitting and installation online, and is now able to manage the ongoing needs of his solar system as well.
That’s a customer journey – and, frankly, a pretty slick one.
HBR identified four keys to effective customer journeys
- Automation: streamlining processes through technology
- Proactive personalization: continuous learning to deeply understand your customers so you can appropriately prepare for – and pitch – the next step you want them to take
- Contextual interaction: understanding where your customer is so you can lead them to the next step
- Journey innovation: continuing to test, learn, and iterate to create new value for the customer and, as a result, for your organization
The point is to move from offering a bunch of products to providing a seamless, end-to-end solution that helps your customer (member) achieve something important to her.
In other words, leading engagement from the outside-in (yes, as in the white paper I co-authored last spring with Anna Caraveli).
Too often, associations focus on our products: we offer an annual conference, a magazine, some books, a webinar series, an awards program, committee volunteering, industry benchmarking and statistics, etc. And we’re organized to provide those products: there’s a membership team, a meetings team, a publications group, the professional development office, data analysts, etc.
Where’s the customer journey? Where’s the solution to a critical problem? Where are the member outcomes?
Absent.
What if we, instead, focused on learning about what our members are trying to accomplish and putting together a customer journey to get them there?
Obviously, in order to figure out what members are trying to accomplish, you have to ask them, and in more in-depth ways than a member satisfaction survey with a bunch of Likert-scale questions. But if you think about it, I’ll bet you could come up with some places to start your research. Your members might want to:
- Find a first job
- Get a promotion
- Build their professional (or personal) network
- Get outside-the-office experiences (leadership, writing, public speaking) to enhance their long-term career prospects
- Support or defeat particular legislation
- Help others in the profession/industry
- Do a better job marketing their business
- Find clients
- Etc….
Organizing to provide a solution to the problem of “I have a degree, but I need help finding my first job” rather than “to run our online career center” is a radical shift that demands different types of skills from differently constituted staff teams.
But the goal is to become a “Level Four” firm, “more attached to producing solutions to customers’ problems than it is to the products and services it offers.” Or, as HBR put it, “Key to these expanded journeys is often their integration with other service providers. Because this increases the value of the journey, carefully handing customers off to another firm can actually enhance the journey’s stickiness…” and with it, member loyalty and enthusiasm and association profitability.
Decision Journey image from the original HBR article cited, “Competing on Customer Journeys“